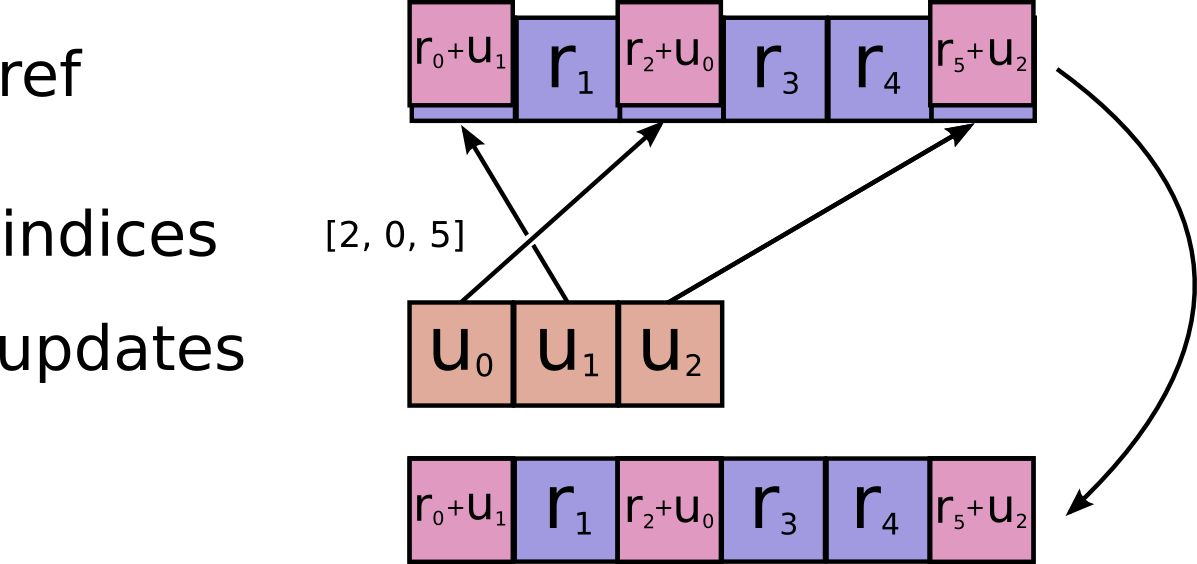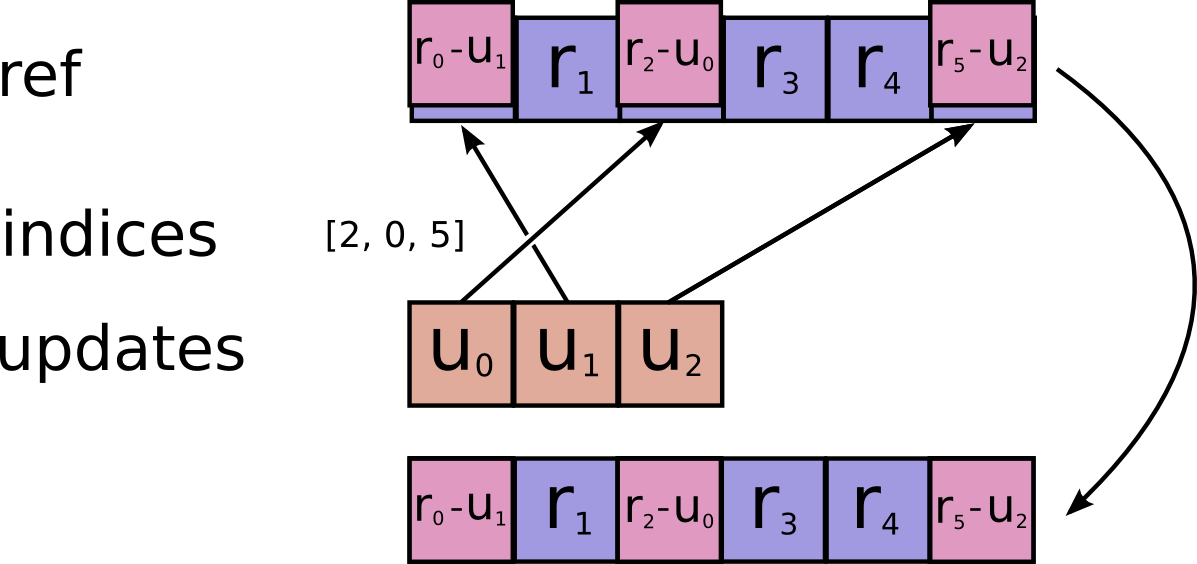# Copyright 2015 The TensorFlow Authors. All Rights Reserved.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
# ==============================================================================
"""Variables.
See the [Variables](https://tensorflow.org/api_guides/python/state_ops) guide.
"""
from __future__ import absolute_import
from __future__ import division
from __future__ import print_function
from tensorflow.python.framework import ops
from tensorflow.python.framework import tensor_shape
from tensorflow.python.ops import array_ops
from tensorflow.python.ops import gen_math_ops
from tensorflow.python.ops import gen_resource_variable_ops
from tensorflow.python.ops import gen_state_ops
# go/tf-wildcard-import
# pylint: disable=wildcard-import
from tensorflow.python.ops.gen_state_ops import *
# pylint: enable=wildcard-import
from tensorflow.python.util.tf_export import tf_export
# pylint: disable=protected-access,g-doc-return-or-yield,g-doc-args
def variable_op(shape, dtype, name="Variable", set_shape=True, container="",
shared_name=""):
"""Deprecated. Used variable_op_v2 instead."""
if not set_shape:
shape = tensor_shape.unknown_shape()
ret = gen_state_ops.variable(shape=shape, dtype=dtype, name=name,
container=container, shared_name=shared_name)
# TODO(mrry): Move this to where it is used, so we can get rid of this op
# wrapper?
if set_shape:
ret.set_shape(shape)
return ret
def variable_op_v2(shape, dtype, name="Variable", container="", shared_name=""):
"""Create a variable Operation.
See also variables.Variable.
Args:
shape: The shape of the tensor managed by this variable
dtype: The underlying type of the tensor values.
name: optional name to use for the variable op.
container: An optional string. Defaults to "".
If non-empty, this variable is placed in the given container.
Otherwise, a default container is used.
shared_name: An optional string. Defaults to "".
If non-empty, this variable is named in the given bucket
with this shared_name. Otherwise, the node name is used instead.
Returns:
A variable tensor.
"""
return gen_state_ops.variable_v2(
shape=shape,
dtype=dtype,
name=name,
container=container,
shared_name=shared_name)
def init_variable(v, init, name="init"):
"""Initializes variable with "init".
This op does the following:
if init is a Tensor, v = init
if callable(init): v = init(VariableShape(v), v.dtype)
Args:
v: Variable to initialize
init: Tensor to assign to v,
Or an object convertible to Tensor e.g. nparray,
Or an Initializer that generates a tensor given the shape and type of v.
An "Initializer" is a callable that returns a tensor that "v" should be
set to. It will be called as init(shape, dtype).
name: Optional name for the op.
Returns:
The operation that initializes v.
"""
with ops.name_scope(None, v.op.name + "/", [v, init]):
with ops.name_scope(name) as scope:
with ops.colocate_with(v):
if callable(init):
assert v.get_shape().is_fully_defined(), "Variable shape unknown."
# TODO(mrry): Convert to v.shape when the property and
# accessor are reconciled (and all initializers support
# tf.TensorShape objects).
value = init(v.get_shape().as_list(), v.dtype.base_dtype)
value = ops.convert_to_tensor(value, name="value")
return gen_state_ops.assign(v, value, name=scope)
else:
init = ops.convert_to_tensor(init, name="init")
return gen_state_ops.assign(v, init, name=scope)
def is_variable_initialized(ref, name=None):
"""Checks whether a tensor has been initialized.
Outputs boolean scalar indicating whether the tensor has been initialized.
Args:
ref: A mutable `Tensor`.
Should be from a `Variable` node. May be uninitialized.
name: A name for the operation (optional).
Returns:
A `Tensor` of type `bool`.
"""
if ref.dtype._is_ref_dtype:
return gen_state_ops.is_variable_initialized(ref=ref, name=name)
# Handle resource variables.
return ref.is_initialized(name=name)
@tf_export(v1=["assign_sub"])
def assign_sub(ref, value, use_locking=None, name=None):
"""Update 'ref' by subtracting 'value' from it.
This operation outputs "ref" after the update is done.
This makes it easier to chain operations that need to use the reset value.
Args:
ref: A mutable `Tensor`. Must be one of the following types:
`float32`, `float64`, `int64`, `int32`, `uint8`, `uint16`, `int16`,
`int8`, `complex64`, `complex128`, `qint8`, `quint8`, `qint32`, `half`.
Should be from a `Variable` node.
value: A `Tensor`. Must have the same type as `ref`.
The value to be subtracted to the variable.
use_locking: An optional `bool`. Defaults to `False`.
If True, the subtraction will be protected by a lock;
otherwise the behavior is undefined, but may exhibit less contention.
name: A name for the operation (optional).
Returns:
Same as "ref". Returned as a convenience for operations that want
to use the new value after the variable has been updated.
"""
if ref.dtype._is_ref_dtype:
return gen_state_ops.assign_sub(
ref, value, use_locking=use_locking, name=name)
return ref.assign_sub(value)
@tf_export(v1=["assign_add"])
def assign_add(ref, value, use_locking=None, name=None):
"""Update 'ref' by adding 'value' to it.
This operation outputs "ref" after the update is done.
This makes it easier to chain operations that need to use the reset value.
Args:
ref: A mutable `Tensor`. Must be one of the following types:
`float32`, `float64`, `int64`, `int32`, `uint8`, `uint16`, `int16`,
`int8`, `complex64`, `complex128`, `qint8`, `quint8`, `qint32`, `half`.
Should be from a `Variable` node.
value: A `Tensor`. Must have the same type as `ref`.
The value to be added to the variable.
use_locking: An optional `bool`. Defaults to `False`.
If True, the addition will be protected by a lock;
otherwise the behavior is undefined, but may exhibit less contention.
name: A name for the operation (optional).
Returns:
Same as "ref". Returned as a convenience for operations that want
to use the new value after the variable has been updated.
"""
if ref.dtype._is_ref_dtype:
return gen_state_ops.assign_add(
ref, value, use_locking=use_locking, name=name)
return ref.assign_add(value)
@tf_export(v1=["assign"])
def assign(ref, value, validate_shape=None, use_locking=None, name=None):
"""Update 'ref' by assigning 'value' to it.
This operation outputs a Tensor that holds the new value of 'ref' after
the value has been assigned. This makes it easier to chain operations
that need to use the reset value.
Args:
ref: A mutable `Tensor`.
Should be from a `Variable` node. May be uninitialized.
value: A `Tensor`. Must have the same type as `ref`.
The value to be assigned to the variable.
validate_shape: An optional `bool`. Defaults to `True`.
If true, the operation will validate that the shape
of 'value' matches the shape of the Tensor being assigned to. If false,
'ref' will take on the shape of 'value'.
use_locking: An optional `bool`. Defaults to `True`.
If True, the assignment will be protected by a lock;
otherwise the behavior is undefined, but may exhibit less contention.
name: A name for the operation (optional).
Returns:
A `Tensor` that will hold the new value of 'ref' after
the assignment has completed.
"""
if ref.dtype._is_ref_dtype:
return gen_state_ops.assign(
ref, value, use_locking=use_locking, name=name,
validate_shape=validate_shape)
return ref.assign(value, name=name)
@tf_export(v1=["count_up_to"])
def count_up_to(ref, limit, name=None):
r"""Increments 'ref' until it reaches 'limit'.
Args:
ref: A Variable. Must be one of the following types: `int32`, `int64`.
Should be from a scalar `Variable` node.
limit: An `int`.
If incrementing ref would bring it above limit, instead generates an
'OutOfRange' error.
name: A name for the operation (optional).
Returns:
A `Tensor`. Has the same type as `ref`.
A copy of the input before increment. If nothing else modifies the
input, the values produced will all be distinct.
"""
if ref.dtype._is_ref_dtype:
return gen_state_ops.count_up_to(ref, limit=limit, name=name)
return gen_state_ops.resource_count_up_to(
ref.handle, limit, T=ref.dtype, name=name)
@tf_export(v1=["scatter_update"])
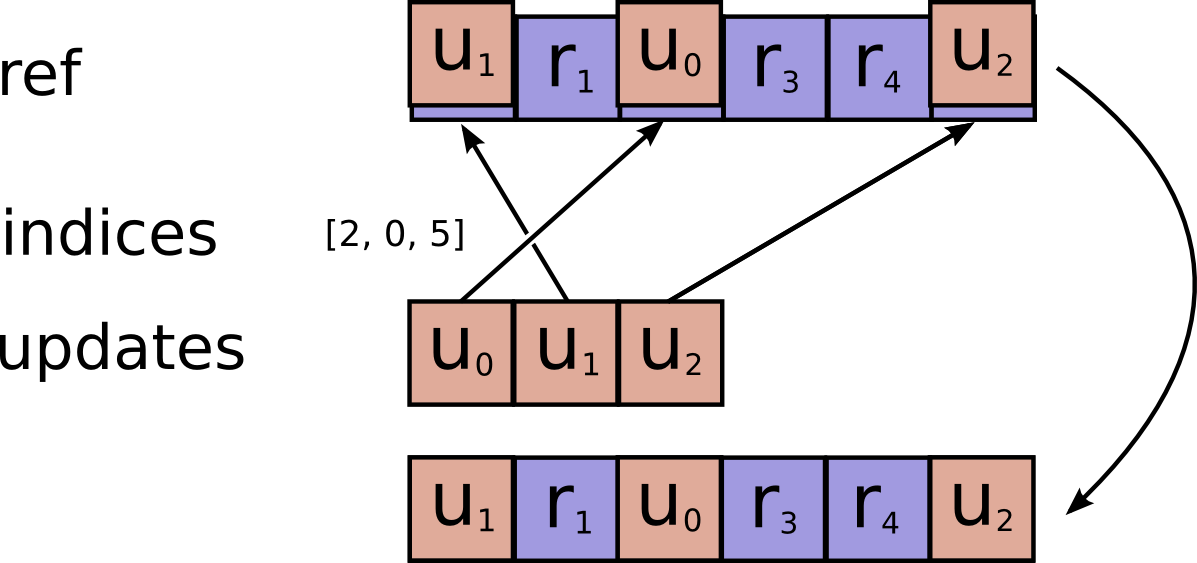
def scatter_update(ref, indices, updates, use_locking=True, name=None):
# pylint: disable=line-too-long
r"""Applies sparse updates to a variable reference.
This operation computes
```python
# Scalar indices
ref[indices, ...] = updates[...]
# Vector indices (for each i)
ref[indices[i], ...] = updates[i, ...]
# High rank indices (for each i, ..., j)
ref[indices[i, ..., j], ...] = updates[i, ..., j, ...]
```
This operation outputs `ref` after the update is done.
This makes it easier to chain operations that need to use the reset value.
If values in `ref` is to be updated more than once, because there are
duplicate entries in `indices`, the order at which the updates happen
for each value is undefined.
Requires `updates.shape = indices.shape + ref.shape[1:]`.
Args:
ref: A `Variable`.
indices: A `Tensor`. Must be one of the following types: `int32`, `int64`.
A tensor of indices into the first dimension of `ref`.
updates: A `Tensor`. Must have the same type as `ref`.
A tensor of updated values to store in `ref`.
use_locking: An optional `bool`. Defaults to `True`.
If True, the assignment will be protected by a lock;
otherwise the behavior is undefined, but may exhibit less contention.
name: A name for the operation (optional).
Returns:
Same as `ref`. Returned as a convenience for operations that want
to use the updated values after the update is done.
"""
if ref.dtype._is_ref_dtype:
return gen_state_ops.scatter_update(ref, indices, updates,
use_locking=use_locking, name=name)
return ref._lazy_read(gen_resource_variable_ops.resource_scatter_update( # pylint: disable=protected-access
ref.handle, indices, ops.convert_to_tensor(updates, ref.dtype),
name=name))
@tf_export(v1=["scatter_nd_update"])
def scatter_nd_update(ref, indices, updates, use_locking=True, name=None):
r"""Applies sparse `updates` to individual values or slices in a Variable.
`ref` is a `Tensor` with rank `P` and `indices` is a `Tensor` of rank `Q`.
`indices` must be integer tensor, containing indices into `ref`.
It must be shape `[d_0, ..., d_{Q-2}, K]` where `0 < K <= P`.
The innermost dimension of `indices` (with length `K`) corresponds to
indices into elements (if `K = P`) or slices (if `K < P`) along the `K`th
dimension of `ref`.
`updates` is `Tensor` of rank `Q-1+P-K` with shape:
```
[d_0, ..., d_{Q-2}, ref.shape[K], ..., ref.shape[P-1]].
```
For example, say we want to update 4 scattered elements to a rank-1 tensor to
8 elements. In Python, that update would look like this:
```python
ref = tf.Variable([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8])
indices = tf.constant([[4], [3], [1] ,[7]])
updates = tf.constant([9, 10, 11, 12])
update = tf.scatter_nd_update(ref, indices, updates)
with tf.Session() as sess:
print sess.run(update)
```
The resulting update to ref would look like this:
[1, 11, 3, 10, 9, 6, 7, 12]
See `tf.scatter_nd` for more details about how to make updates to
slices.
Args:
ref: A Variable.
indices: A `Tensor`. Must be one of the following types: `int32`, `int64`.
A tensor of indices into ref.
updates: A `Tensor`. Must have the same type as `ref`.
A Tensor. Must have the same type as ref. A tensor of updated
values to add to ref.
use_locking: An optional `bool`. Defaults to `True`.
An optional bool. Defaults to True. If True, the assignment will
be protected by a lock; otherwise the behavior is undefined,
but may exhibit less contention.
name: A name for the operation (optional).
Returns:
The value of the variable after the update.
"""
if ref.dtype._is_ref_dtype:
return gen_state_ops.scatter_nd_update(
ref, indices, updates, use_locking, name)
return ref._lazy_read(gen_state_ops.resource_scatter_nd_update( # pylint: disable=protected-access
ref.handle, indices, ops.convert_to_tensor(updates, ref.dtype),
name=name))
@tf_export(v1=["scatter_add"])
def scatter_add(ref, indices, updates, use_locking=False, name=None):
# pylint: disable=line-too-long
r"""Adds sparse updates to the variable referenced by `resource`.
This operation computes
```python
# Scalar indices
ref[indices, ...] += updates[...]
# Vector indices (for each i)
ref[indices[i], ...] += updates[i, ...]
# High rank indices (for each i, ..., j)
ref[indices[i, ..., j], ...] += updates[i, ..., j, ...]
```
This operation outputs `ref` after the update is done.
This makes it easier to chain operations that need to use the updated value.
Duplicate entries are handled correctly: if multiple `indices` reference
the same location, their contributions add.
Requires `updates.shape = indices.shape + ref.shape[1:]`.
Args:
ref: A `Variable`.
indices: A `Tensor`. Must be one of the following types: `int32`, `int64`.
A tensor of indices into the first dimension of `ref`.
updates: A `Tensor`. Must have the same type as `ref`.
A tensor of updated values to store in `ref`.
use_locking: An optional `bool`. Defaults to `False`.
If True, the assignment will be protected by a lock;
otherwise the behavior is undefined, but may exhibit less contention.
name: A name for the operation (optional).
Returns:
Same as `ref`. Returned as a convenience for operations that want
to use the updated values after the update is done.
"""
if ref.dtype._is_ref_dtype:
return gen_state_ops.scatter_add(ref, indices, updates,
use_locking=use_locking, name=name)
return ref._lazy_read(gen_resource_variable_ops.resource_scatter_add( # pylint: disable=protected-access
ref.handle, indices, ops.convert_to_tensor(updates, ref.dtype),
name=name))
@tf_export(v1=["scatter_nd_add"])
def scatter_nd_add(ref, indices, updates, use_locking=False, name=None):
r"""Applies sparse addition to individual values or slices in a Variable.
`ref` is a `Tensor` with rank `P` and `indices` is a `Tensor` of rank `Q`.
`indices` must be integer tensor, containing indices into `ref`.
It must be shape `[d_0, ..., d_{Q-2}, K]` where `0 < K <= P`.
The innermost dimension of `indices` (with length `K`) corresponds to
indices into elements (if `K = P`) or slices (if `K < P`) along the `K`th
dimension of `ref`.
`updates` is `Tensor` of rank `Q-1+P-K` with shape:
```
[d_0, ..., d_{Q-2}, ref.shape[K], ..., ref.shape[P-1]].
```
For example, say we want to add 4 scattered elements to a rank-1 tensor to
8 elements. In Python, that update would look like this:
```python
ref = tf.Variable([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8])
indices = tf.constant([[4], [3], [1] ,[7]])
updates = tf.constant([9, 10, 11, 12])
add = tf.scatter_nd_add(ref, indices, updates)
with tf.Session() as sess:
print sess.run(add)
```
The resulting update to ref would look like this:
[1, 13, 3, 14, 14, 6, 7, 20]
See `tf.scatter_nd` for more details about how to make updates to
slices.
Args:
ref: A mutable `Tensor`. Must be one of the following types: `float32`,
`float64`, `int32`, `uint8`, `int16`, `int8`, `complex64`, `int64`,
`qint8`, `quint8`, `qint32`, `bfloat16`, `uint16`, `complex128`, `half`,
`uint32`, `uint64`. A mutable Tensor. Should be from a Variable node.
indices: A `Tensor`. Must be one of the following types: `int32`, `int64`.
A tensor of indices into ref.
updates: A `Tensor`. Must have the same type as `ref`.
A tensor of updated values to add to ref.
use_locking: An optional `bool`. Defaults to `False`.
An optional bool. Defaults to True. If True, the assignment will
be protected by a lock; otherwise the behavior is undefined,
but may exhibit less contention.
name: A name for the operation (optional).
Returns:
A mutable `Tensor`. Has the same type as `ref`.
"""
if ref.dtype._is_ref_dtype:
return gen_state_ops.scatter_nd_add(
ref, indices, updates, use_locking, name)
return ref._lazy_read(gen_state_ops.resource_scatter_nd_add( # pylint: disable=protected-access
ref.handle, indices, ops.convert_to_tensor(updates, ref.dtype),
name=name))
@tf_export(v1=["scatter_sub"])
def scatter_sub(ref, indices, updates, use_locking=False, name=None):
r"""Subtracts sparse updates to a variable reference.
```python
# Scalar indices
ref[indices, ...] -= updates[...]
# Vector indices (for each i)
ref[indices[i], ...] -= updates[i, ...]
# High rank indices (for each i, ..., j)
ref[indices[i, ..., j], ...] -= updates[i, ..., j, ...]
```
This operation outputs `ref` after the update is done.
This makes it easier to chain operations that need to use the reset value.
Duplicate entries are handled correctly: if multiple `indices` reference
the same location, their (negated) contributions add.
Requires `updates.shape = indices.shape + ref.shape[1:]` or
`updates.shape = []`.
Args:
ref: A mutable `Tensor`. Must be one of the following types: `float32`,
`float64`, `int32`, `uint8`, `int16`, `int8`, `complex64`, `int64`,
`qint8`, `quint8`, `qint32`, `bfloat16`, `uint16`, `complex128`, `half`,
`uint32`, `uint64`. Should be from a `Variable` node.
indices: A `Tensor`. Must be one of the following types: `int32`, `int64`.
A tensor of indices into the first dimension of `ref`.
updates: A `Tensor`. Must have the same type as `ref`.
A tensor of updated values to subtract from `ref`.
use_locking: An optional `bool`. Defaults to `False`.
If True, the subtraction will be protected by a lock;
otherwise the behavior is undefined, but may exhibit less contention.
name: A name for the operation (optional).
Returns:
A mutable `Tensor`. Has the same type as `ref`.
"""
if ref.dtype._is_ref_dtype:
return gen_state_ops.scatter_sub(ref, indices, updates,
use_locking=use_locking, name=name)
return ref._lazy_read(gen_resource_variable_ops.resource_scatter_sub( # pylint: disable=protected-access
ref.handle, indices, ops.convert_to_tensor(updates, ref.dtype),
name=name))
@tf_export(v1=["scatter_nd_sub"])
def scatter_nd_sub(ref, indices, updates, use_locking=False, name=None):
r"""Applies sparse subtraction to individual values or slices in a Variable.
`ref` is a `Tensor` with rank `P` and `indices` is a `Tensor` of rank `Q`.
`indices` must be integer tensor, containing indices into `ref`.
It must be shape `[d_0, ..., d_{Q-2}, K]` where `0 < K <= P`.
The innermost dimension of `indices` (with length `K`) corresponds to
indices into elements (if `K = P`) or slices (if `K < P`) along the `K`th
dimension of `ref`.
`updates` is `Tensor` of rank `Q-1+P-K` with shape:
```
[d_0, ..., d_{Q-2}, ref.shape[K], ..., ref.shape[P-1]].
```
For example, say we want to subtract 4 scattered elements from a rank-1 tensor
to 8 elements. In Python, that update would look like this:
```python
ref = tf.Variable([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8])
indices = tf.constant([[4], [3], [1] ,[7]])
updates = tf.constant([9, 10, 11, 12])
op = tf.scatter_nd_sub(ref, indices, updates)
with tf.Session() as sess:
print sess.run(op)
```
The resulting update to ref would look like this:
[1, -9, 3, -6, -6, 6, 7, -4]
See `tf.scatter_nd` for more details about how to make updates to
slices.
Args:
ref: A mutable `Tensor`. Must be one of the following types: `float32`,
`float64`, `int32`, `uint8`, `int16`, `int8`, `complex64`, `int64`,
`qint8`, `quint8`, `qint32`, `bfloat16`, `uint16`, `complex128`, `half`,
`uint32`, `uint64`. A mutable Tensor. Should be from a Variable node.
indices: A `Tensor`. Must be one of the following types: `int32`, `int64`.
A tensor of indices into ref.
updates: A `Tensor`. Must have the same type as `ref`.
A tensor of updated values to add to ref.
use_locking: An optional `bool`. Defaults to `False`.
An optional bool. Defaults to True. If True, the assignment will
be protected by a lock; otherwise the behavior is undefined,
but may exhibit less contention.
name: A name for the operation (optional).
Returns:
A mutable `Tensor`. Has the same type as `ref`.
"""
if ref.dtype._is_ref_dtype:
return gen_state_ops.scatter_nd_sub(
ref, indices, updates, use_locking, name)
return ref._lazy_read(gen_state_ops.resource_scatter_nd_sub( # pylint: disable=protected-access
ref.handle, indices, ops.convert_to_tensor(updates, ref.dtype),
name=name))
@tf_export("batch_scatter_update")
def batch_scatter_update(ref, indices, updates, use_locking=True, name=None):
"""Generalization of `tf.scatter_update` to axis different than 0.
Analogous to `batch_gather`. This assumes that `ref`, `indices` and `updates`
have a series of leading dimensions that are the same for all of them, and the
updates are performed on the last dimension of indices. In other words, the
dimensions should be the following:
`num_prefix_dims = indices.ndims - 1`
`batch_dim = num_prefix_dims + 1`
`updates.shape = indices.shape + var.shape[batch_dim:]`
where
`updates.shape[:num_prefix_dims]`
`== indices.shape[:num_prefix_dims]`
`== var.shape[:num_prefix_dims]`
And the operation performed can be expressed as:
`var[i_1, ..., i_n, indices[i_1, ..., i_n, j]] = updates[i_1, ..., i_n, j]`
When indices is a 1D tensor, this operation is equivalent to
`tf.scatter_update`.
To avoid this operation there would be 2 alternatives:
1) Reshaping the variable by merging the first `ndims` dimensions. However,
this is not possible because `tf.reshape` returns a Tensor, which we
cannot use `tf.scatter_update` on.
2) Looping over the first `ndims` of the variable and using
`tf.scatter_update` on the subtensors that result of slicing the first
dimension. This is a valid option for `ndims = 1`, but less efficient than
this implementation.
See also `tf.scatter_update` and `tf.scatter_nd_update`.
Args:
ref: `Variable` to scatter onto.
indices: Tensor containing indices as described above.
updates: Tensor of updates to apply to `ref`.
use_locking: Boolean indicating whether to lock the writing operation.
name: Optional scope name string.
Returns:
Ref to `variable` after it has been modified.
Raises:
ValueError: If the initial `ndims` of `ref`, `indices`, and `updates` are
not the same.
"""
with ops.name_scope(name):
indices = ops.convert_to_tensor(indices, name="indices")
indices_shape = array_ops.shape(indices)
indices_dimensions = indices.get_shape().ndims
if indices_dimensions is None:
raise ValueError("batch_gather does not allow indices with unknown "
"shape.")
nd_indices = array_ops.expand_dims(indices, axis=-1)
nd_indices_list = []
# Scatter ND requires indices to have an additional dimension, in which the
# coordinates of the updated things are specified. For this to be adapted to
# the scatter_update with several leading dimensions, we simply make use of
# a tf.range for all the leading dimensions followed by concat of all the
# coordinates we created with the original indices.
# For example if indices.shape = [2, 3, 4], we should generate the following
# indices for tf.scatter_nd_update:
# nd_indices[:, :, 0] = [[0, 0, 0], [1, 1, 1]]
# nd_indices[:, :, 1] = [[0, 1, 2], [0, 1, 2]]
# nd_indices[:, :, 2] = indices
for dimension in range(indices_dimensions - 1):
# In this loop we generate the following for the example (one for each
# iteration).
# nd_indices[:, :, 0] = [[0, 0, 0], [1, 1, 1]]
# nd_indices[:, :, 1] = [[0, 1, 2], [0, 1, 2]]
# This is done at every iteration with a tf.range over the size of the
# i-th dimension and using broadcasting over the desired shape.
dimension_size = indices_shape[dimension]
shape_to_broadcast = [1] * (indices_dimensions + 1)
shape_to_broadcast[dimension] = dimension_size
dimension_range = array_ops.reshape(
gen_math_ops._range(0, dimension_size, 1), shape_to_broadcast)
if dimension_range.dtype.base_dtype != nd_indices.dtype:
dimension_range = gen_math_ops.cast(dimension_range, nd_indices.dtype)
nd_indices_list.append(
dimension_range * array_ops.ones_like(nd_indices))
# Add the original indices at the end, as described above, and concat.
nd_indices_list.append(nd_indices)
final_indices = array_ops.concat(nd_indices_list, axis=-1)
return scatter_nd_update(
ref, final_indices, updates, use_locking=use_locking)